Shape Scholarship
Shape Scholarship - For example, output shape of dense layer is based on units defined in the layer where as output shape of conv layer depends on filters. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. I am wondering what is the main difference between shape = 19, shape = 20 and shape = 16? In python, i can do this: I'm new to python and numpy in general. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? In my android app, i have it like this: So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first dimension of. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. Another thing to remember is, by default, last. I read several tutorials and still so confused between the differences in dim, ranks, shape, aixes and dimensions. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first dimension of. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? In python, i can do this: Data.shape() is there a similar function in pyspark? A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. In my android app, i have it like this: And i want to make this black. Another thing to remember is, by default, last. In r graphics and ggplot2 we can specify the shape of the points. I read several tutorials and still so confused between the differences in dim, ranks, shape, aixes and dimensions. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. In my android app, i have it like this: I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. Another thing to remember is, by default, last. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. I do not see a single function that can do this. I. For example, output shape of dense layer is based on units defined in the layer where as output shape of conv layer depends on filters. I am wondering what is the main difference between shape = 19, shape = 20 and shape = 16? A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. Data.shape() is there a similar function in. In r graphics and ggplot2 we can specify the shape of the points. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. I read several tutorials and still so confused between the differences in dim, ranks, shape,. For example, output shape of dense layer is based on units defined in the layer where as output shape of conv layer depends on filters. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first dimension of. Another thing to remember is, by default, last. I already know how to set the. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first dimension of. In r graphics and ggplot2 we can specify the shape of the points.. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. I am trying to find out the size/shape of a dataframe in pyspark. In my android app, i have it like this: A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. Data.shape() is there a similar function in pyspark? Another thing to remember is, by default, last. A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. I'm new to python and numpy in general. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0,. And i want to make this black. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? I do not see a single function that can do this. In python, i can do this: I'm new to python and numpy in general. Data.shape() is there a similar function in pyspark? I am wondering what is the main difference between shape = 19, shape = 20 and shape = 16? I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. In python, i can do this: A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first dimension of. In r graphics and ggplot2 we can specify the shape of the points. I do not see a single function that can do this. For example, output shape of dense layer is based on units defined in the layer where as output shape of conv layer depends on filters. I am trying to find out the size/shape of a dataframe in pyspark. Data.shape() is there a similar function in pyspark? Another thing to remember is, by default, last. In my android app, i have it like this: And i want to make this black. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d.How Organizational Design Principles Can Shape Scholarship Programs
How Does Advising Shape Students' Scholarship and Career Paths YouTube
Enter to win £500 Coventry University Student Ambassador Scholarship
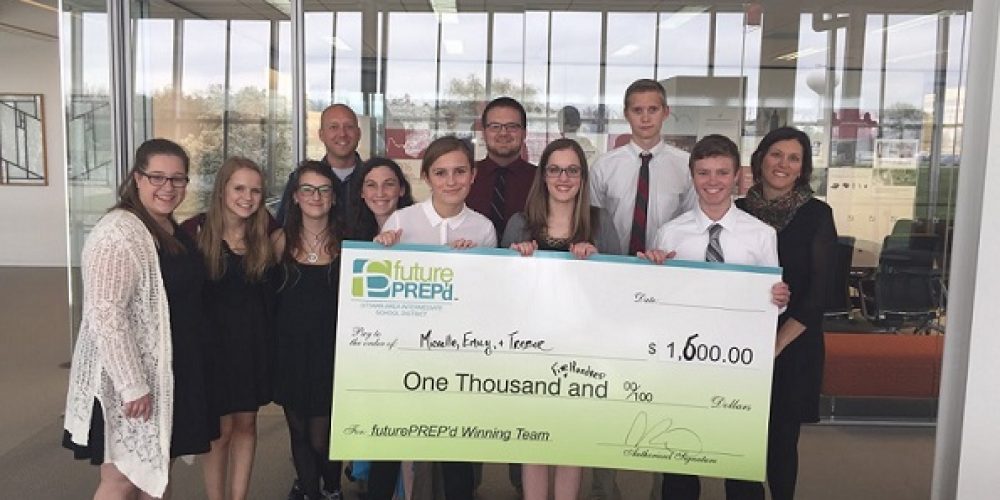
Shape’s FuturePrep’D Students Take Home Scholarships Shape Corp.
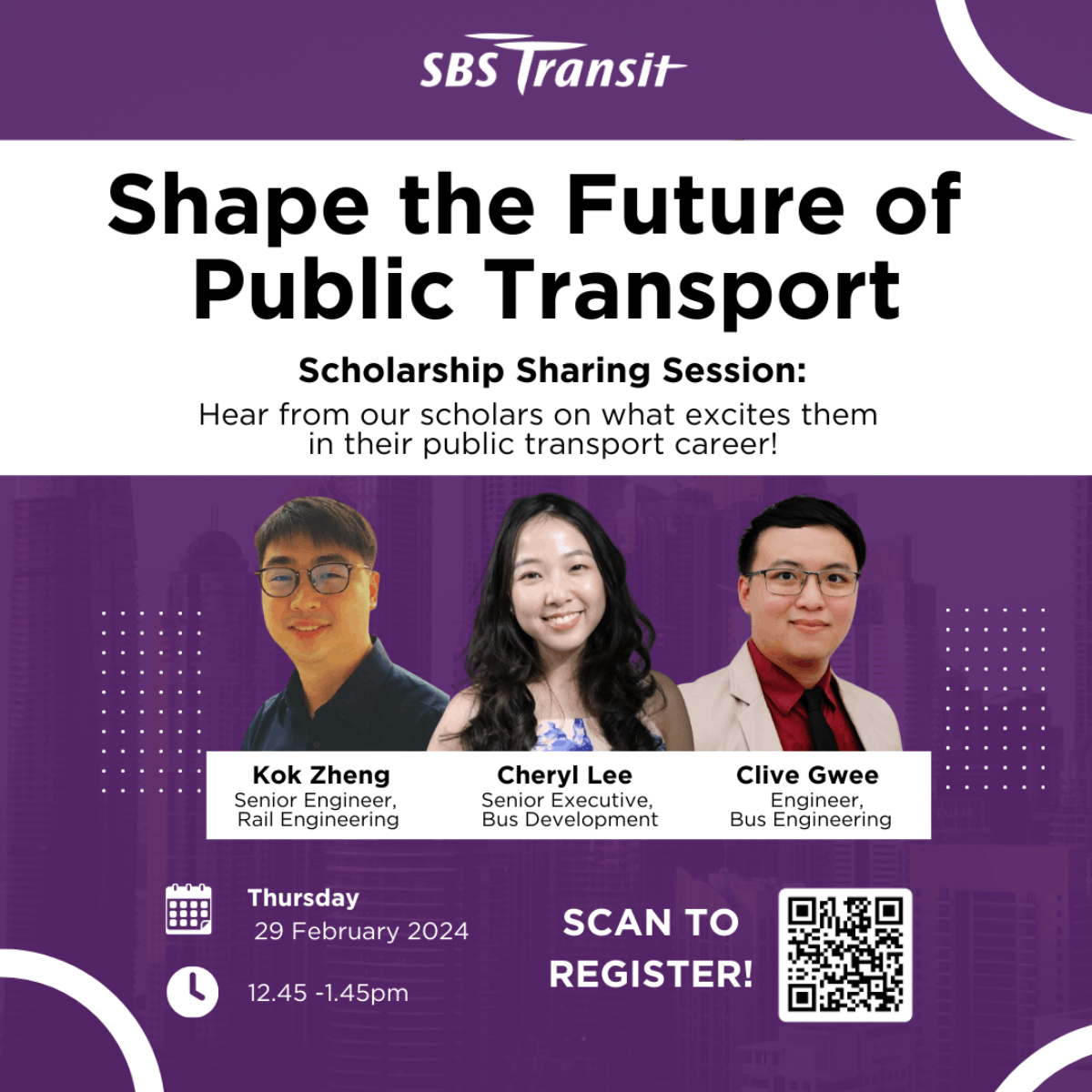
Shape the Future of Public Transport SBS Transit SgIS Scholarship
SHAPE Scholarship Boksburg
Top 30 National Scholarships to Apply for in October 2025
14 SHAPE Engineering students awarded the EAHK Outstanding Performance
SHAPE America Ruth Abernathy Presidential Scholarships
SHAPE Scholarship Boksburg
Shape Is A Tuple That Gives You An Indication Of The Number Of Dimensions In The Array.
I'm New To Python And Numpy In General.
I Read Several Tutorials And Still So Confused Between The Differences In Dim, Ranks, Shape, Aixes And Dimensions.
I Am Wondering What Is The Main Difference Between Shape = 19, Shape = 20 And Shape = 16?
Related Post:






.jpg)

